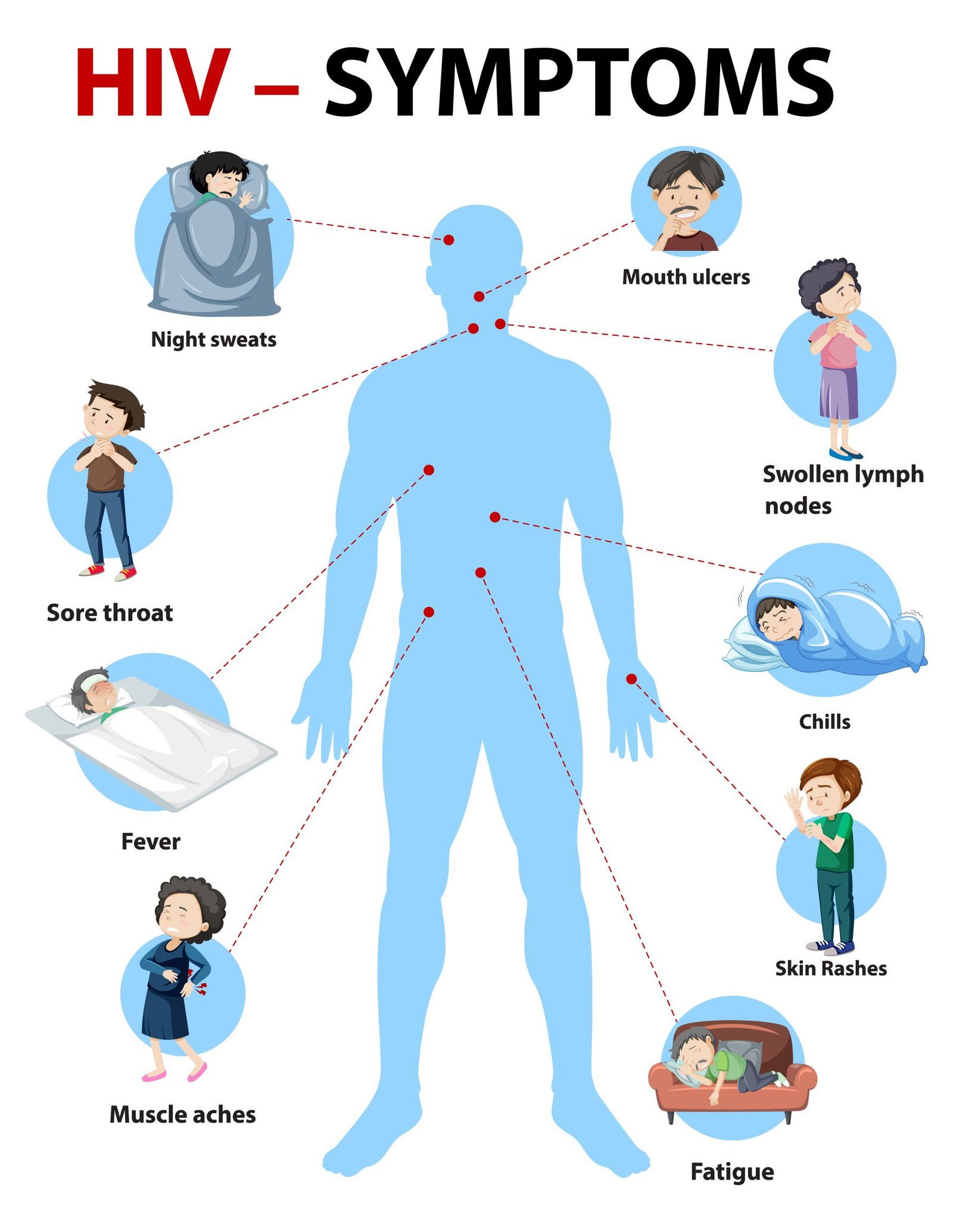
The first sign of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infection can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms initially. However, within a few weeks to months after contracting the virus, some people may experience flu-like symptoms, known as acute retroviral syndrome (ARS). These symptoms can include:
Symptoms of HIV infection infographic illustration
1. Fever: Often accompanied by chills and night sweats.
2. Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired or lacking energy.
3. Sore throat: Persistent or severe throat discomfort.
4. Swollen lymph nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes, commonly in the neck, armpits, or groin.
5. Body aches and joint pain: Generalized muscle or joint discomfort.
6. Rash: Skin rash that may appear red, raised, or with small bumps.
7. Headache: Persistent or severe headaches.
8. Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea: Digestive symptoms may occur.
It’s important to note that these symptoms are not unique to HIV and can be caused by various other illnesses. Therefore, experiencing these symptoms alone is not a definitive indicator of HIV infection. The only way to confirm HIV infection is through specific tests that detect the presence of the virus or antibodies to the virus in the body.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to HIV or are concerned about your risk, it’s crucial to seek medical advice and get tested for HIV. Early detection, diagnosis, and access to appropriate care can greatly improve health outcomes for individuals with HIV.
“In such a case Prakasine would be much beneficial”
